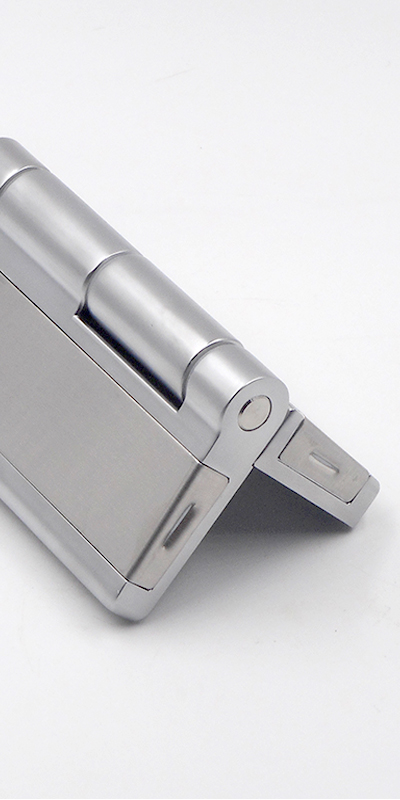
Friction hinges are widely used in industrial settings where controlled motion and precise positioning are essential.
Friction hinges hold doors, panels, lids, or screens in place at any angle without the need for external support. They use internal resistance to maintain position during movement, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring consistent torque and minimal maintenance.
Understanding how friction hinges function can help engineers and buyers make better hardware decisions.
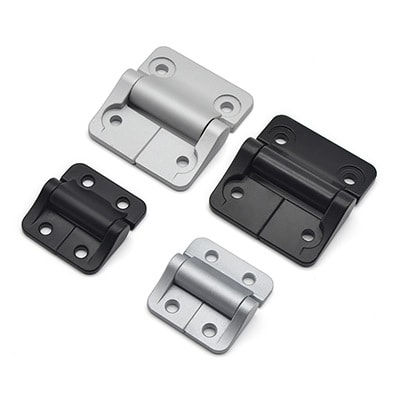

What Are Friction Hinges?
Friction hinges—also known as torque hinges—are mechanical components that use internal friction to resist movement. Unlike traditional hinges that swing freely, friction hinges apply resistance throughout their range of motion, allowing objects like access panels, inspection covers, or display monitors to stay in place at any angle without external props.
Friction hinges, also called torque hinges, use internal friction to hold panels, lids, or screens in position without external support. Unlike free-swinging hinges, they maintain position throughout motion.
These hinges are often used in equipment enclosures, electronics, and medical devices where stability, quiet operation, and safety are critical. For example, when integrated into a laptop hinge or a testing cabinet lid, the hinge ensures the cover stays open or moves smoothly without slamming shut. This ability to stay in place reduces wear and tear on the structure and improves the user experience.
Friction hinges come in various sizes, torque ratings, and materials depending on their intended environment. Some even offer specialized configurations such as soft close hinges, which use hydraulic damping for gentle closing, especially beneficial in environments where shock or vibration must be minimized.
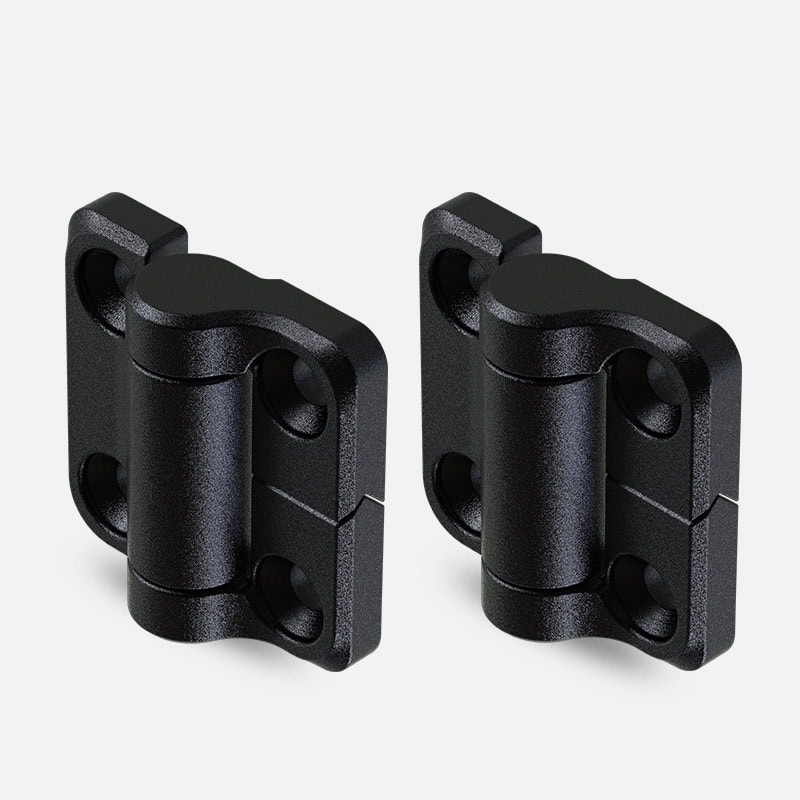

Where Are Friction Hinges Used in Industry?
Friction hinges are designed to serve specialized roles in a variety of industrial sectors. These include electronics, aerospace, automotive, marine, and testing equipment manufacturing. Their unique ability to hold panels or covers in place without external support makes them especially useful in tight or constrained environments.
In industry, friction hinges are used in control panels, medical devices, vehicle compartments, and test equipment—anywhere secure positioning and motion control are required.
Let’s look at a few practical examples:
-
Medical Devices: Friction hinges are integrated into diagnostic machines and portable medical carts to hold screens and panels open during operation.
-
Test Equipment: Constant temperature and humidity chambers often use friction hinges for maintenance access panels, where doors must stay open safely without external holders.
-
Transportation: In buses, aircraft, and ships, friction hinges are used in overhead compartments, seating systems, and instrument panels for ergonomic positioning.
In rugged environments such as marine applications, marine hinges with integrated friction elements are favored due to their corrosion resistance and stability under dynamic loads. Similarly, outdoor industrial hinges may also incorporate friction control to prevent panels from being blown shut by wind or vibration.
Are Friction Hinges Adjustable?
Yes, many friction hinges are built with adjustable torque mechanisms that allow users to fine-tune the level of resistance. This is particularly beneficial in environments where the load or operating angle may change over time, requiring a different amount of holding force.
Yes, adjustable friction hinges allow users to fine-tune torque using built-in screws, offering custom motion resistance for precise positioning.
These adjustable models typically feature a central screw or dial that modifies the internal tension applied to the moving parts. When tightened, the hinge increases resistance; when loosened, it decreases resistance. This design is especially popular in machinery access panels, folding industrial desks, and high-use electronic enclosures.
Take for example a heavy duty hinge used on a large industrial enclosure. The ability to control how easily the door opens or closes can improve both safety and efficiency for maintenance staff. Adjustable torque options also extend hinge lifespan, as the wear is evenly distributed, and operational pressure can be balanced against environmental conditions.
How Long Do Friction Hinges Last?
Friction hinges are known for their durability, especially when selected appropriately for the application and maintained correctly. Their lifespan is typically measured in opening-and-closing cycles, which can range from tens of thousands to over a million operations, depending on the build quality and operating conditions.
Friction hinges typically last for 50,000 to over 200,000 cycles, depending on materials, environment, and design specifications.
Factors that influence hinge longevity include:
-
Material composition: Stainless steel or aluminum hinges last longer in corrosive environments.
-
Usage frequency: High-cycle applications require heavy-duty components with robust internal mechanisms.
-
Environmental exposure: Dust, moisture, and temperature extremes can impact performance over time.
In outdoor or marine applications, using corrosion resistant hinges ensures the hinge retains its torque characteristics over time. Additionally, proper lubrication, especially in heavy duty truck door hinge applications, significantly extends hinge life by reducing wear from repetitive motion and environmental exposure.

Benefits of Friction Hinges in Industrial Equipment
Friction hinges offer a series of advantages over traditional hinges in industrial use. From improving safety to enhancing user ergonomics, these benefits make them indispensable in modern engineering.
Friction hinges offer stable positioning, reduce component count, enhance ergonomics, and prevent accidental closure—ideal for industrial use cases.
Here are some key advantages:
-
Stable Motion Control: Friction hinges prevent accidental closing or opening, reducing safety risks.
-
Improved Ergonomics: Operators can adjust screens or panels without needing to hold them in place.
-
Maintenance-Free Design: Many models, such as aluminum geared continuous hinges, are designed to operate without lubrication.
-
Design Flexibility: Engineers can integrate them into custom assemblies without needing gas struts or stays.
-
Space Efficiency: They eliminate the need for additional holding mechanisms, streamlining equipment layout.
For example, in test chambers or industrial ovens where panel positioning is crucial, friction hinges reduce downtime and enhance ease of use. Additionally, components like detachable hinges can be combined with friction mechanisms for applications requiring frequent removal and reattachment of access panels.
Conclusion
Friction hinges are essential in industrial design for secure, adjustable, and ergonomic motion control. Their durability and functionality make them a top choice for various precision equipment and enclosures.




