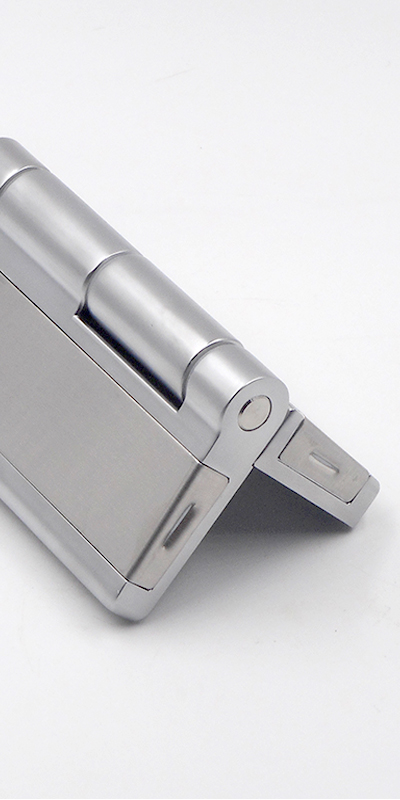
Electrified butt hinges transmit power from frame to door for access control—safely and invisibly.
An electrified butt hinge allows low-voltage power to pass from the door frame to the door leaf, enabling operation of electronic devices such as electric locks, card readers, or sensors. It replaces surface wiring and keeps power transmission hidden and secure in industrial door systems.
Let’s explore how these hinges are built, how they work, and how to choose the right one for your industrial needs.
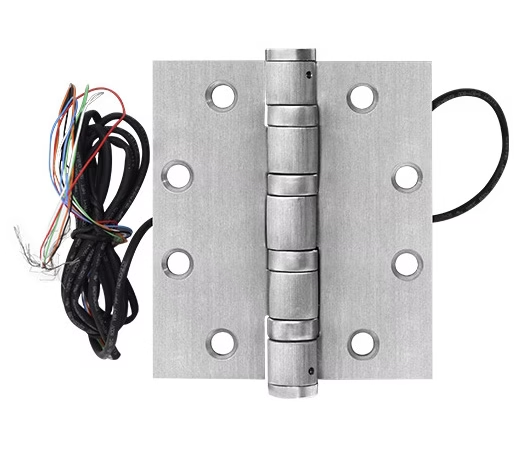
What Is an Electrified Butt Hinge?
Electrified butt hinges are standard hinges integrated with wiring that allows power and data transmission between a stationary frame and a moving door. Designed for use in high-security or electronically controlled industrial environments, they eliminate the need for exposed wires, maintaining both function and appearance. An electrified butt hinge is a standard hinge integrated with concealed wiring that transmits electrical power or signals from the frame to devices on the door.
This type of hinge is commonly used in industrial doors equipped with electronic locks, sensors, alarms, and automated access systems. For example, electronic testing chambers, factory security doors, or telecom enclosures often require uninterrupted electrical current for operational continuity. Electrified hinges ensure power is delivered directly through the hinge mechanism—concealed and tamper-resistant.
Some hinges even feature ball-bearing mechanisms for smooth movement and extended life under heavy load, similar to heavy duty exterior door hinges used in rugged industrial doors. These enhancements make them ideal for frequent-use environments where performance and durability are critical.
How Does an Electrified Butt Hinge Work?
Electrified butt hinges maintain a continuous electrical connection between the frame and the door while allowing the door to swing open and closed. They are designed to transfer low-voltage power for devices like electric strikes, magnetic locks, and keypads. The hinge works by housing concealed wires that transfer power and data between the frame and the moving door, maintaining continuous electrical connection during door movement.
A typical hinge contains flexible, multi-stranded wires running through the hinge knuckle and into the leaves. These wires carry voltage, usually 12VDC or 24VDC, which powers devices mounted on the door. Because the wires are hidden within the hinge, they’re protected from wear, vandalism, and environmental exposure.
This concealed design ensures operational reliability and keeps the door’s appearance clean and professional. In contrast to external conduit or door loops, which are vulnerable to damage, electrified hinges offer a more secure and integrated solution—similar in concept to Adjustable Torque Stainless Steel Hinges that combine structure and control in one component.
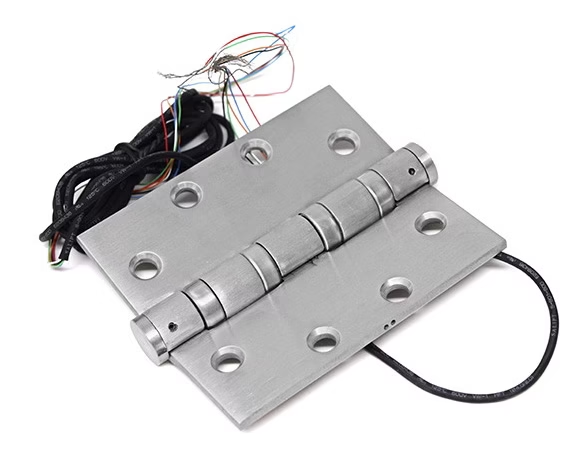
Types of Electrified Hinges for Industrial Doors
Electrified hinges come in several forms to meet different industrial needs. The most common include electrified butt hinges, power transfer hinges, and motorized hinges. Each type offers different features for load handling, current capacity, and application environments. Common types include standard electrified butt hinges, continuous power transfer hinges, and motorized hinges, each suited to different industrial use cases.
| Type | Best For | Voltage Support | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrified Butt Hinge | Standard Industrial Doors | 12V/24V DC | Simple concealed power transfer |
| Power Transfer Hinge (EPT) | Heavy Security or High Traffic Doors | Up to 10A | More robust and secure connections |
| Motorized Hinge | Robotic or Automated Doors | Variable | Enables motion and power delivery |
For heavy or oversized industrial doors, electrified heavy duty continuous hinges or Heavy Duty Detachable Barrel Hinges can be adapted with built-in wiring channels to combine structural support and power transfer. Some continuous hinges are UL-rated and provide up to 100,000 open/close cycles—ideal for demanding B2B environments.
Electrified Hinges vs. Other Power Transfer Methods
Though electrified butt hinges are highly effective, they are one of several power transfer methods used in electronic door systems. Others include electric power transfer (EPT) devices, door loops, and surface-mounted wiring. Unlike surface-mounted wires or electric power transfer (EPT) devices, electrified hinges provide seamless, tamper-resistant power delivery within the hinge itself.
EPTs, for example, are mounted in the door edge or frame and use spring-loaded contacts to maintain electrical continuity. While robust, they often require more complex door modifications. Door loops, although inexpensive, expose wires to physical damage and wear, making them unsuitable for industrial environments where rugged reliability is necessary.
On the other hand, electrified hinges require no visible wiring and often support retrofit applications. They’re ideal for upgrading security without altering the door’s structure—particularly in environments where aesthetics and tamper-resistance are priorities. This solution is often preferred when companies need to Replace Industrial Door Hinges while integrating electronic functionality.
Considerations When Choosing an Electrified Butt Hinge
Selecting the right hinge involves more than just size and finish. You need to consider load capacity, power requirements, door usage frequency, and compatibility with access control components. Select hinges based on door weight, voltage needs, current rating, and compatibility with your access control hardware.
-
Electrical Load: Verify that the hinge supports your door hardware’s voltage and amperage requirements. Most hinges can carry 0.5A to 3A, but some industrial models support more.
-
Door Type & Weight: For heavy or high-use industrial doors, use hinges rated for frequent cycles and large loads, like those seen with Weld-on hinges in industrial applications.
-
Wiring Needs: Some hinges come pre-wired with 2, 4, or 8-conductor cables, offering flexibility for power and data transmission.
-
Material & Finish: For corrosive or marine environments, 316 stainless models offer better resistance—similar to 316 Stainless Marine Friction Hinges used in ocean-side applications.
Compatibility with control systems and lock types is also key. For example, if using electric strikes instead of magnetic locks, make sure the hinge supports the required load and control voltage.
Conclusion
Electrified butt hinges ensure reliable power transfer in industrial doors without compromising security or design integrity.




